Ruby OO
Ruby的OO实在是个常聊常新的话题。
Ruby号称是完全的面向对象编程语言,”一切皆对象”,所以在Ruby的世界里,你总是可以问:”对象在哪里?”
对象、类、超类
首先列出一张我见过比较好的Ruby类的关系图:
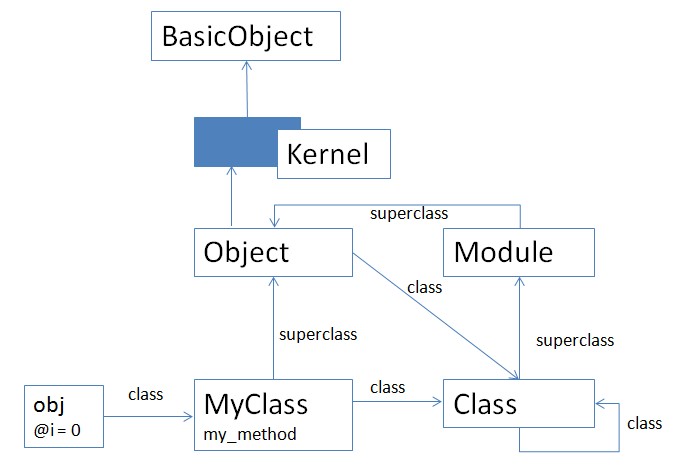
这张图比较清晰的展示了对象,对象的类,Class,Module,Object,Kernel,BasicObject之间的关系。
经常有人混淆的一点是:instance_of 和 subclass,前者是实例与对象的关系,后者是继承的关系。
实例与实例之间共享相同的方法,所以方法并不定义在某个实例中,而是定义在类中。类与类之间在允许情况下可以共享方法,这就有了继承的关系。
AccessControl
在一个类中,方法根据多大程度向外展示,可以分为三种:
- public (default) 没有任何限制
- protected 只能被定义类的对象,或者定义类的子类们的对象所调用 Access is kept within the family.
- private
只能在当前对象的上下文中使用
« Programming Ruby » : “ Can be called only in functional form (that is, with an implicit self as the receiver). Private methods therefore can be called in the defining class and by that class’s descendents and ancestors, but only within the same object.”
只能通过函数式进行调用(即隐式的self),因此也可以在定义的类和其子类内部使用。
作为动态语言,Ruby只有当你试图访问受限方法时,才会提示权限错误。
获取对象方法
通过Ruby的内省方式我们可以得到一个对象的方法:
从对象的角度
- methods
官方文档:Returns a list of the names of public and protected methods of obj. This will include all the methods accessible in obj’s ancestors. If the all parameter is set to false, only those methods in the receiver will be listed. - private_methods
官方文档:Returns the list of private methods accessible to obj. If the all parameter is set to false, only those methods in the receiver will be listed. - protected_methods
- public_methods
从类的角度看
- instance_methods
Returns an array containing the names of the public and protected instance methods in the receiver. - private_instance_methods Returns a list of the private instance methods defined in mod
- protected_instance_methods
- public_instance_methods
Kernel
实际上,Object的实例方法都是定义在Module Kernel中的, Objece通过include将Kernel中的实例方法变为了自身的。
这个地方不深究其实也没啥大不了的东西,一深究就会发现水很深…
首先我们来看Ruby怎么实现include:
Ruby implements include very simply: the module that you include is effectively added as a superclass of the class being defined. It’s as if the module was the parent of the class that it is mixed in to.
就是当你include AMod时候,等同于Ruby搞了个类作为当前类的父类就完事了。
另外一点是:Module must itself hold a link to the original parent class.
这句话第一次看的时候感觉也是废话,因为只有这样才能把ancestor chain链接起来嘛。但是细思恐极,因为下面这个例子就是这句话的真实体现……
如果想要在Object里面添加方法,可以这样做:
module New
def new_method
end
end
module Kernel
include New
end
new_method
由于脚本中默认的main是Object的实例,而Object继承自Kernel,BasicObject,所以在Kernel中include新增的new_method方法后,在脚本里就可以直接使用new_method了。
这逻辑是不是很巧妙?
但是上面这段代码在脚本里执行出错==!:undefined local variable or method new_method for main:Object
因为你还需要加上一段:
class Object
include Kernel
end
原因其实也没啥滑头,大家自己考虑吧。
Singleton Class
定义singleton methods
- class Singleton
def Singleton.one()
end
end - module Other
def two() end
end - class « Singleton
include Other
def one()
end
end - Singleton.extend Other
- def Singleton.one()
end
通过Object#singleton_methods用于查看对象上的singleton methods
What is it
singleton method的实现方式,跟Module类似,当定义singleton method时,就会插入a new anonymous class到inheritance hierarchy。
singleton method是针对对象的。很多人会说,singleton method不是用来定义类方法嘛?
所谓的类,是指share同样的方法到不同的实例,但是singleton method只是为specific的对象服务的,让定义了singleton method的特定对象显得special。从这个角度讲,所谓的类方法,只是singleton method的一小部分。
include & extend
Object#extend:Adds to obj the instance methods from each module given as a parameter. extend就是将molude中的实例方法作为obj的singleton method.不管你的receiver是obj还是class,本质上都是obj
Object#singleton_class可以返回一个ojb的singleton class,如果这个obj没有实例类,则这个方法会创建一个新的实例类。
可以利用这个方法动态的为对象添加方法:
module B
def newone
“newone”
end
end
obj.singleton_class.send :include, B
obj.newone #=> “newone”
这样,我们就可以动态的为特定的obj添加不同模块中的方法了
关于singleton method,可以参考http://www.devalot.com/articles/2008/09/ruby-singleton